Back to: O level Biology NOTES Uganda syllabus
KINGDOM: PLANTAE
The kingdom Plantae comprises a variety of plants.
General characteristics
- They are mostly green in colour thus carry out photosynthesis
- They are multicellular.
- They exhibit; limited movements such as opening and closing of petals etc.
- Their cells aresurrounded by cellulose cell wall.
- They respond slowly to external stimuli and do not move from one place to another.The kingdom is sub divided into three divisions, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, spermatophyta and the algae.
Spirogyra
Characteristics of spirogyra
- It is filamentous green algae found in fresh water of slow flowing water in ponds, streams, and lakes
- It grows in length and its always one cell thick.
- Each cell is capable of living an independent life
- Each cell has one spiral chloroplast from one end to another
- Small protein bodies called pyrenoids are present on each ribbon like chloroplast and are used to store starch
- The nucleus is in the center to control the activities of the cell
- There is a gelatinous sheath(mucilage) around the cells that gives them slimy nature that is useful for protection
Reproduction in Spirogyra.
1.Asexual reproduction
The vegetative reproduction is common and consists of partof the filament breaking off and continuing to live as a separate plant. It can also be called fragmentation.
2.Sexual reproduction
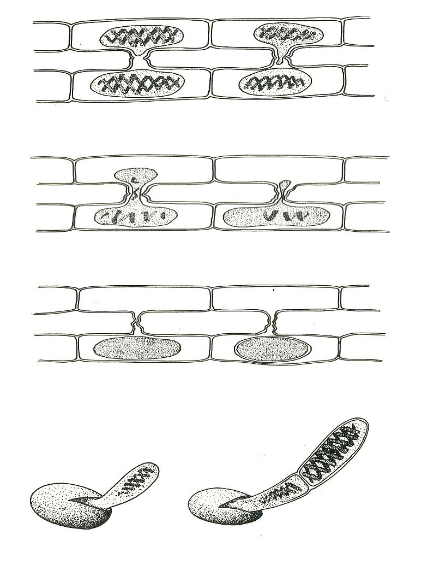
Spirogyra reproduces by conjugation between filaments lying side by side as follows;
- The opposite cells of the two different filaments lying side by side develop a swelling or an out-growth which begins to grow towards each other.
- On touching they dissolve to form a conjugation tube and at the same time the contents change into gametes.
- The gametes from one cell (male gamete) migrate through the conjugation tube to another cell (female) gamete.
- The two gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops a thick resistant wall and becomes a zygospore.
- When the conditions are favorable, the zygospore germinates and grows into another filament.

Economic importance
- Algae are used in the manufacture of gar
- They provide food for humans and fish.
- When they die, they sink at the bottom of the sea bed on which they can turn into oil.
- During photosynthesis, they release oxygen that is necessary for the respiration of animals that live in water.
- They are used in the manufacture ice cream, cosmetics, and plants.
- They pollute water, i.e. producing foul smell.
- They clog water pipes in hindering the flow of water
DIVISION: BRYOPHYTA
The division is comprised of liverworts and moss plants.
Main characteristics
- They have simple leaves and rhizoids that are root-like structures. They are used mainly for anchorage.
- Plants lack vascular bundles thus depend on diffusion for movement of materials.
- They are photosynthetic.
- They are found in sheltered and wet areas.
- Their life cycle consists of the two generations which alternate a gametophyte and sporophyte generation
Examples are mosses and liverworts which belong to 2 classes; musci and hepatica respectively.
DIVISION: TRACHEOPHYTA
These show alternation of generations. The sporophytes differentiate into roots, stems andleaves with lignified vascular tissues that are used for conducting water and food.This division is divided into 2 sub-phyla:
1.Pteridophyta
2.Spermatophyta
Pteridophyta
This is made up of ferns. Ferns are commonly found in shaded places which are damp with cool temperature. Some ferns grow on trees as epiphytes.The body of a sporophyte fern is divided into leaves, stems and roots. The leaves are called fronds while the stems are rhizomes. The spore forming structures are called sporophyta which occur on the underneath (side) of a frond in clusters called sori.
Main characteristics
- The sporophyte is the dominant generation while gametophyte generation is short lived.
- The rhizomes grow horizontally below the soil surface.
- Ferns have well-delivered conducting tissues i.e. vascular bundles. The xylem also supports the plants.
- They have the adventitious roots which anchor the plants into the soil and absorb materials
DIVISION: SPERMATOPHYTA
The spermatophyta comprises of well-developed plants which are adapted to a variety of habitats. The habitats include terrestrial and aquatic.The seed are either contained inside the ovary wall or exposed.
General characteristics
- The body is divided into leaves, stem and root system
- Plants have complex and well developed vascular tissues.
- The supporting tissues like xylem, sclerenchyma and collenchyma, are found in leaves, stem and roots. Turgid parenchyma cells also provide support.
- Reproduce sexually.
- Sporophyte generation is greatly reduced and short-lived( flower)
The division is subdivided into two sub divisions:
Gymnospermae (cone bearing plants)
These are commonly found in high lands/ altitudes areas. They show xerophytic characteristics such as sunken stomata, needle-like leaves, thick waxy cuticle to prevent or reduce rate of transpiration.Examples include pines, cypress, cedar tree, cycads, jacaranda, and bougainvillea.Gymnospermae refers to plants whose seeds are not enclosed.
Main characteristics
- They are non-flowering plants.
- Their seeds are found in the cone scale.
- Have needle like leaves which reduce the rate of transpiration.
- Found in high altitudes and can carry out photosynthesis at low temperatures.
Angiospermae (flowering plants)
These are flowering plants where seeds are enclosed in the ovary of the fruits
General characteristics
- They are flowering plants
- Their seeds are enclosed in the ovary from where the fruits develop
- The reproductive organs are found within the flower
These are sub divided into two classes. Monocotyledonae and dicotyledonae.
Monocotyledonae
These are mainly grass family. Examples include wheat, rice, barley, star grass, sorghum, maize, millet sugarcane etc
Distinguishing characteristics
- Seeds have one cotyledonHave fibrous root system
- Have parallel veins in their leaves
- Leaves are generally narrow and long.
- Vascular bundles are scattered in the stem cross section
- Lack vascular cambium, i.e. no secondary thickening of the stem.
- Flowers are held on an inflorescence.
- The floral parts are in threes or multiples of threes.
Dicotyledonae
These include herbs, shrubs and trees. Herbs are non woody plants so turgidity of cells supports them. Shrubs and trees have stems with supporting tissues such as xylem.Examples include beans, jacaranda, hibiscus, etc.
Distinguishing characteristics
- Have seeds with two cotyledons
- They have tap root system.
- Have network (reticulate) venation.
- Leaves are generally broad and short.
- Vascular bundles are radially arranged in the stem cross section.
- Have vascular cambium for secondary thickening.
- The floral parts are in fours or fives or in their multiples.
Question
State the differences between monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants.
