Back to: O level Biology NOTES Uganda syllabus
Examples of protoctists are:
Amoeba, Euglena, Paramecium, Trypanasomes, Chlamydomonas, etc.

Main features of Protoctista
- They are unicellular organisms i.e. single celled organisms.
- They have a true nucleus with a nuclear membrane.
- They have double membrane organelles.
- Some members locomote freely using either pseudopodia (false legs) in amoeba, cilia in paramecium or flagella in euglena and trypanosomes.
- They have varied forms of nutrition e.g. euglena and chlamydomonas make their own food by photosynthesis, amoeba and paramecium by phagocytosis and simple absorption of digested food by trypanosomes.
- They live mostly in water or watery environments like wet lands.
PHYLUM PROTOZOA
This is the main phylum of kingdom Protoctista. It has several classes but the most important are:
- Rhizopoda e.g. AmoebaThese are free living organisms by means of pseudopodia or false legs
- Ciliophora (ciliata) e.g. parameciumThese possess cilia all over the body for locomotion or movement.
- Mastigophora e.g. trypanosomes.These have a flagellum for locomotion.
General characteristics of protozoans
- They are unicellular.
- They are mainly found in fresh or marine water and in the soil.
- They are mostly free-living but some are parasites.
- They carry out locomotion by means of flagella, cilia or pseudopodia.
- Euglena have autotrophs and others protozoa-such as amoeba.
- They reproduce asexually by binary fission or multiple fission.
Examples of protozoa include Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, Trypanosome and plasmodium
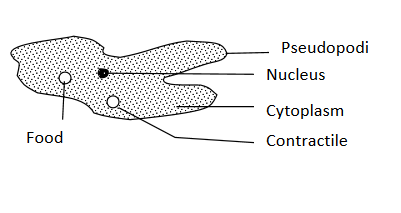
1.Amoeba
Amoeba is a free-living protozoa found at the bottom of ponds. It has temporary extensions called pseudopodia used for locomotion. The pseudopodia are also used for enclosing food particles which form food vacuoles. The food in vacuole is digested by phagocytosis.The extra amount of water can be regulated by contractile vacuole
Structure of amoeba
Locomotion in amoeba:
Amoeba moves by means of pseudopodia (false legs) that are formed by the flow of cytoplasm (plasmosol and plasmogel) in the direction of movement but this is followed by the flow of other protoplasm in the same direction, as shown be:
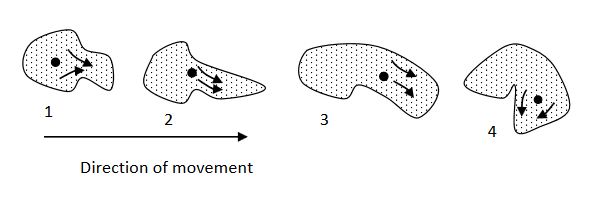
The movement of amoeba is mainly determined by factors e.g. water, food, poison, acidity, alkalinity, etc. and it will make amoeba move towards or away from such factors.
Excretion in amoeba
Excess water is eliminated from its body by contractile vacuole. This collects the water and moves from cell membrane where it discharges its contents. The process is repeated and hence it is the means of osmoregulation by amoeba. Other by-products diffuse out of the cytoplasm through the cell membrane e.g. CO2.
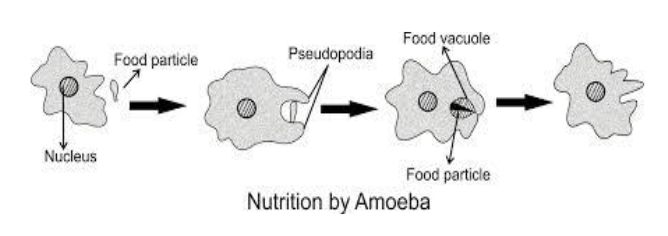
Feeding
Amoeba feeds on microscopic algae and bacteria. It captures the food by developing pseudopodia around the food and it engulfs it. The cytoplasm flows around the food. This one now forms the food vacuole.Digestive enzymes are produced which break the food particles into soluble food substances. The products are utilized and amoeba moves away from undigestedfood remains. This is called egestion.
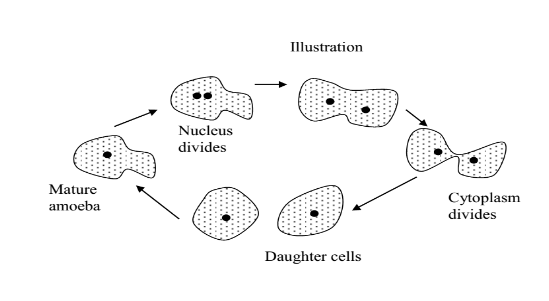
Reproduction in amoeba
Amoeba reproduces by binary fission.
Binary fission in amoeba;
- An amoeba ready to reproduce stops moving and rounds off.
- The nucleus then constricts and divides into two identical parts. This will be followed by nucleus complete separation as the cytoplasm begins to constrict so that the separation of the remaining parts into 2 can occur.
- Two identical daughter amoebae forms and move apart to feed and grow into mature amoebae before they divide again.
2.Paramecium
Paramecium uses cilia for movement and collection of food. It has special row of cilia that waft food particles into the hollow gullet. The food vacuoles move in a very definite path through it and egestion occurs atonly one point near the region of ingestion.
Structure of paramecium
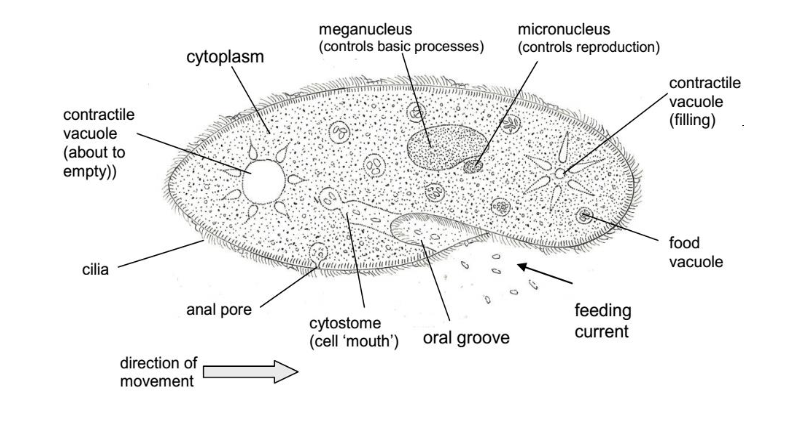
Unlike amoeba, paramecium has a distinct and permanent shape and certain areas of cytoplasm, (cell organelles), are specialised to carry out specific functions
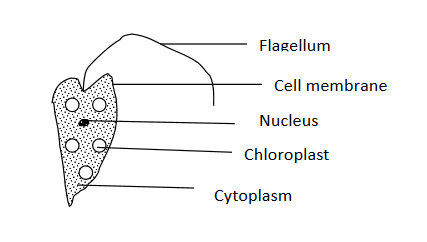
3.Euglena
This is commonly found in water and in soil. It is photosynthetic and moves by means of flagellum.
Structure of euglena