Back to: PRIMARY SIX SCIENCE LESSON NOTES
Seeds.
A seed is a developed fertilized ovule
A seed is a mature fertilized ovule
Groups of seeds
Monocotyledonous seeds
Dicotyledonous seeds
Monocotyledonous seeds
Monocotyledonous seeds are seeds with only one cotyledon
These are also called cereals or grains
Examples of monocotyledonous seeds
- Maize seed
- Millet seed
- Oat seed
- Wheat seed
- Rice seed
- Sorghum seed
- Barley seed
Structure of a maize seed.

Functions if each part of a maize seed
Endosperm
Endosperm stores food for the plant
Plumule
Plumule develops into a shoot system
Cotyledon
Cotyledon absorbs food from endosperm and supplies to the embryo during germination
Radicle
Radicle develops into a root system
Embryo
This is made up of the plumule and radicle
Embryo develops into a new plant
Testa (seed coat)
Testa protects the inner parts of the seed
Style scar
Style scar is the part where the style was attacked
Stalk scar
Stalk scar attaches
Note
- Plumule sheath protects the plumule
- Radicle sheath protects the radicle
- A maize is a fruit because it has two scar
Dicotyledonous seeds
Dicotyledonous seeds are seeds with two cotyledons
Examples of dicotyledonous seeds
- Coffee seeds
- Beans
- Soya bean seeds
- Groundnut
- Simsim
- Mango seed
- Orange seed
- Avocado
- Tomatoes
- Cowpeas.
Structure of a bean seed

Function of each part of a bean seed
Testa (seed coat)
Testa protects the inner parts of a bean seed
Cotyledon
Cotyledon provides food to the germinating embryo
GERMINATION IN PLANTS
- Germination is the development of a seed embryo into a seedling under favourable conditions.
- During germination, the Radicle grows into the root system to support the seedling firmly into the soil.
- The radicle also grows root hairs to absorb water and mineral salts from soil.
Types of germination.
There are basically two types of germination
- Epigeal germination
- Hypogeal germination
Epigeal germination is a type of germination where the cotyledon comes out of the ground.
Epigeal germination is a common characteristic of dicotyledonous seeds eg. Beans, soy beans, groundnuts.
structure showing the different stages in Epigeal germination.

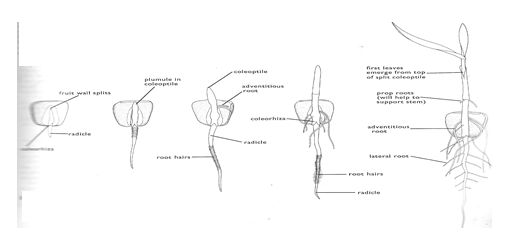
Hypogeal germination:
This is a type of germination in which the cotyledon remains under the ground
This type of germination is a common characteristic of monocotyledonous seeds.
Examples include; maize, millet, rice, sorghum etc.
Conditions necessary for seed germination.
- A seed will only germinate under favourable conditions such as, oxygen, water and warmth.
Seed viability is the ability of a seed to germinate under favourable conditions.
A viable seed should be;
- Mature and dry
- Whole without a hole / wrinkles
- Health and of a good variety
