Back to: PRIMARY SIX SCIENCE LESSON NOTES
Types of pollination.
There are two types of pollination namely;
- Self pollination
- Cross pollination
Self pollination
is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther heads to the stigma of the same flower
Flowers with self pollination have shorter stigma compared to their anther heads.
They also have brightly coloured petals to attract pollinators
Adaptation of flowers to self-pollination
The others and the stigma mature at the some flower.
The flower remain closed until self pollination has taken place.
The flower is hermaphrodite i.e It has both male and female parts.
Some flower are buried in the ground until self pollination takes place.
Structure illustrating self-pollination.

W – Petals
X – Anthers
Y– Anther head
Z – Stigma
Examples of self-pollination.
Bean plant
Ground nut plant.
Simsim plant
Tomato plant
Advantages of self pollination
It helps to maintain pure breeds.
Disadvantages of self-pollination.
Flowers are difficult to pollinate because stamen sometimes donot mature at the same time as the as the pistils.
CROSS POLLINATION.
CROSS POLLINATION. Primary six science Notes.Is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther heads of one flower to the stigma of another flower but of the same type or species?
In cross–pollination, the anther heads are shorter than the stigma. https://revisionug.com/
Adaptation of flowers for cross pollination
The male and female flower occur on the same plant but mature at different time’s .i.e. the stamen may mature earlier than the pistil. E.g. maize.
The male and female flower occur on separate plants e.g. pawpaw.
The pollen grains cannot germinate on the stigma of the same flowers and if they do, fertilization cannot occur e.g. passion fruits flower.
Characteristics of cross pollination
Styles are longer than filament
Pistil and stamen are on different flowers
Reduce small amount of the grains
Stigma are higher than anthers
Advantages of cross pollination
Cross pollination can result into new materials
Cross pollination results into healthier seeds and plants
Distance of cross pollination
Cross pollination into undesirable plants reeds
Examples of plants that undergo cross pollination
Maize plants
Coconut
Pawpaw
Cow peas
Passion fruit
Illustration of cross pollination
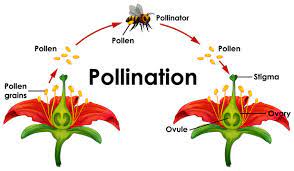

Agent of pollination
These are ways or factors responsible for the transfer of grains from the another stigma.
Agents of pollination
- Winds
- Insects
- Flowing water
- Animals
- Birds
Wind
When winds blows, pollen is transferred from another to the stigma of a flower hence pollination takes place
Characteristics of wind pollinated flowers
- Flowers are small and not easily seed
- Flowers have a dull coloured petals
- Flowers do not produce nectar
- Flowers do not have pollen grains
- Flowers have small and smooth and light pollen grains
- The flowers do not have a smell
- Flowers have long stigma to increase chances of pollen sticking to them
Insects
Insects are able to pollinate flowers as they visit them to collect nectar
Insects rub themselves on the anthers so on the visiting another flowers or carrying out of the flower or coming of the very flower, pollination takes place
Examples of insect pollinated flowers during day time
- Honey bees
- Butter flies
- Beetles
Examples of insects that pollinate flowers during night
Moths
Characteristics of insect pollinated flower
- Flowers are large and easily
- Flowers have brightly coloured petals
- Flowers are well
- Flowers have nectar which is produced by nectarines
- Flower have broad compact sticky stigma
- Flowers have large rough and heavy pollen grains
- The anthers produce few pollen grains
- The stamens have short filaments
Birds
Birds also visit flower to get nectar which they feed on
Flowers pollinated by birds are brightly coloured
As birds are to get nectar they rub their bodies on the anthers and the stigma in the way like insects
Birds that pollinate flowers have long slender breaks which are adapted to sucking nectars from the base of the petal when found
Examples of bird that pollinate flowers
- Sun birds
- Humming birds
Water
Some water plants are pollinated by flowing water
The pollen floats on the top of water until if finds the stigma of such flowers
Examples of water pollinated flowers
- Water lily
- Plankton
- Water hyacinth
Animals
Some eating bats help in pollinating flower because they have hairy bodies on which pollen is attached
Fertilization
Fertilization is the union of the nuclei of the male and female gametes or cell to form a zygote or embryo
Fertilization takes place in the ovary
Male reproductive cells are pollen grains and female cells are ovules
Importance of pollination
- Pollination allows fertilization to take place in crops
- Pollination allows high yields in farmer’s harvest
Uses of flowers to man
- Flowers are used for decoration
- Some flowers are used as insecticides
- Some flowers are used for making dyes
- Some flowers are used as source of income after sale
- Some flower are also used as gifts to friends
- Some flowers are also eaten as food
- Some flowers are used for making colours
Uses of flowers to plants
- Flowers produce seeds and fruits
- Flowers attract pollinators
