Back to: Primary six social studies / p6 sst notes
PHYSICAL FEATURES IN EAST AFRICA.
Physical features are natural land forms of an area.
EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL FEATURES IN EAST AFRICA.
- High lands /mountains
- Rift valley
- Plataeu
- Coastal plains
- Lakes and Rivers
- Plains and inselbergs.
THE MAP OF E.AFRICA SHOWING MAJOR PHYSICAL REGION.
Questions.
- What are physical features?
- Mention five examples of natural lands forms inE.A.
- Identiy any two physical features found on the border of Uganda and DRC.
HIGHLAND MOUNTAINS ;
- These are regions raised between 3000m-5000m above the sea level.
- They are categorised into two depending on their formation ie volcanic and block/horst.
VOLCANIC MOUNTAINS;
- These were formed as a result of volcanic eruption.
- Volcanicity is the proccess by which magma (molten rocks) erupts from underground into the earth crust.
EXAMPLES OF VOLCANOES.
- Mt.Elgon
- Mt.Mufumbirro
- Mt.Kilimanjaro
- Mt.Moroto
- Mt.Meru etc
Other features formed as a result of volcanicity are;
- Plugs eg Tororo rocks.
- Crater eg L.Katwe, Ngorongoro, and Mt.Elgon crater.
- Hot springs eg kitagata, Nakuru Hot springs, Sempaya hotsprings
- Lava plains.
TYPES OF VOLCANIC MOUNTAINS IN E.A.
- Active volcanic mountains (mts that may erupt any time).eg mt.Mufumbiro.
- Dormant (sleeping) volcanic mountains (mountains which erupted in the last 500 years and might still erupt in future).eg. Mt.Kenya, Mt.Kilimanjaro, Mt. Meru.
- Extinct (dead) volcanic mountains (mountains which have stoppederupting) eg Mt.Elgon, Mt. Moroto.
DIAGRAM SHOWING AN ERUPTING VOLCANO.
QUESTIONS.
1. What is meant by the term volcanic mountains?
2. Identify any two volcanic mountains found inE.A.
3. Why is it not advisable for people to stay near an active volcano?
4. What is Magma?
BLOCK MOUNTAINS IN E.A.
- These are mountains which were formed as a result of faulting.
- Faulting is the breaking/cracking the rocks of the earth due to the influence of underground forces.
- Block mountains are sometimes called Horst mountains.
EXAMPLES OF BLOCK MTS/HORST MTS.
- Mt.Rwenzori in Uganda.
- Usambara ranges in Tanzania.
- Ulunguru mts in Tanzania.
- Mt. Nyeru in Kenya
- Mt. Rungwe in Tanzania
- Mt. Kipengere in Tanzania
FORMATION OF BLOCK MOUNTAINS.
There are two theories that explain the formation of the block mts.
- Tension theory
- Compression theory.
- TENSION THEORY
- It stresses the formation of Block Mountains due to tension forces underground.
- The tension forces pulls the rocks underground apart which causes the central block to remain still while the side block sink thus leading to the formation of horst mts.
DIAGRAM SHOWING THE FORMATION OF BLOCK MTS
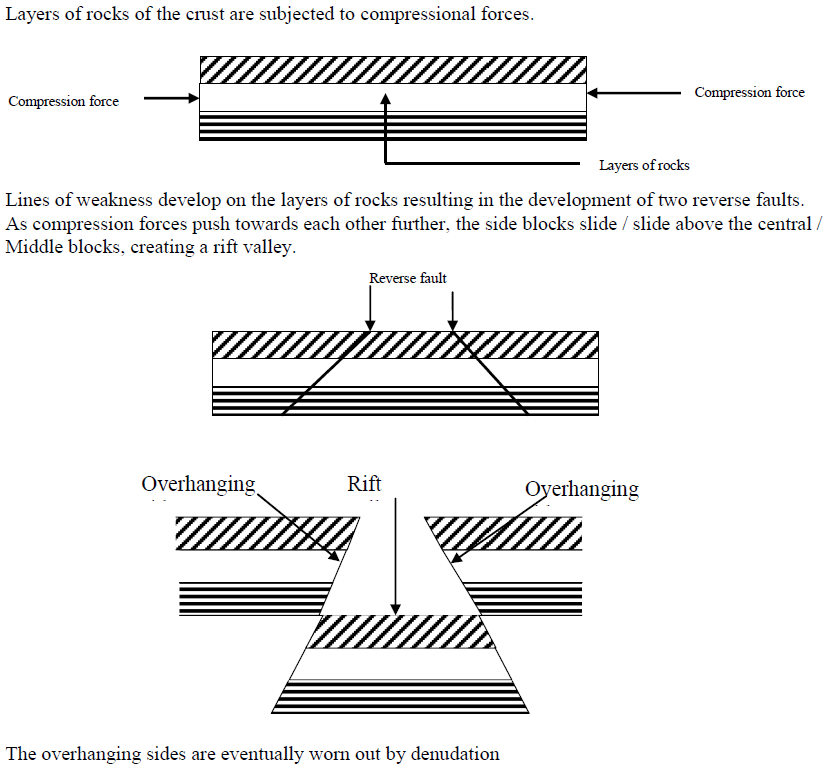
B) COMPRESSION THEORY
- It stresses the formation of horst mountains due to Compression forces underground.
- These forces push the rocks underground from opposite direction causing the middle block to be uplifted and weakens other rocks around it which areeroded hence causing the formation of Block Mountains.
- Other features formed by aprocess of faulting are;
- Rift valley
- Escarpment
- Fault lakes(rift valley lakes )
DIAGRAM SHOWING THE FORMATION OF BLOCK MOUNTAINS USING COMPRESSION THEORY.
IMPORTANCES/VALUES OF HIGHLANDS.
- They help in the formation of rain.
- They are used as mining places.
- They serve as a natural boundary between countries.
- They have features of tourist attractions.
- They are used to construct communication boosters.
- Some Mt.slopes are used for farming.
- They are sources or some rivers.
PROBLEMS FACING PEOPLE WHO LIVE NEAR MTS.
- Severe soil erosion
- Landslides
- Barriers to good road network(make road construction difficulty)
- Some active volcanoes may erupt causing death and destruction of property.
- They hinder agricultural mechanisation since there steepy.
- They hinder people settlement.
Questions.
1. How was the formation of mt.kilimanjaro similar to that of mt.Kenya?
2. What common feature is found on top of dormant volcanoes?
3. How is the formation of mt.Usambara different from that of mt.Moroto?
4. Give one way in which mts hinder the development of agriculture.
5. State the political importance of mts to EastAfrican countries.
6. State any two economic values of mts in E.Africa.
7. How do mts affect the development of transport system?
RIFT VALLEY
- This is along depression on the earth surface with steep called Escarpements. It was formed by faulting..
- The Great African rift valley stretches from Jordan in Asia and enters Africa through Ethiopia and lake Turkana in E. Africa..
- It is divided into two arms (branches) ie.Eastern and western arm.
- The Eastern arm stretches frrom L.Turkana in the north to L.Malawi in the south and ends in R.Zambezi in Mozambique.
Characteristics of a rift valley
- It is long
- It is wide
- It has steep sides called escarpments.
LAKES FOUND IN THE EASTERN ARM.
L.Nakuru L.Baringo L. Naivasha
L.Eyasi L. Magadi L. Natron
L.Magadi L. Manyara
L.Natron
- The western arm starts from north of L.Malawi up to the point of Albert.
- Lakes found in the western arm include;
- L.Tanganyika.
- L.katwe(though is a crater lake)
- L.kivu
- L.Albert
- L.Edward.
- Lake George
NOTE
The steep sides of a rift valley are called escarpments eg. Butiaba and the Mau escarpments in Kenya.
ACTIVITIES DONE IN THE RIFTVALLEY;
- Fishing
- Mining
- Tourism
- Transport
- Farming (pastoralism)
NOTE.
- The Great EastAfrican rift-valley is one of the physical features shared by the E.African countries .In addition to L.Victoria and East African plateau.
- It is not suitable for human settlement due to warm temperatures experienced there caused by low latitude.
A DIAGRAM SHOWING THE FORMATION OR THE RIFT VALLEY.
THE PLATEAU
- A Plateau is a fairly a raised flat topped piece of land.
- It is sometimes called a table land because of its raised nature and flat top.
- The top of the plateau is interrupted by hills and low lands.
- There are also rivers, lakes in low lands and valleys on the plateau.
- The plateau of E.Africa is divided into two namely;
a) THE EASTERN PLATEAU
It occupies Eastern and southern Kenya and comes immediately after the coastal plain its commonly known as Nyika plateau in Kenya and Foreland plateau in TAnzania.
B) THE CENTRAL PLATEAU;
It lies much in the central and western part of Basement complex.
NOTE;
ACTIVITIES DONE ON THE PLATEAU REGIONS OF EAST AFRICA.
- Farming
- Fishing
- Lumbering
- Trade
- Industrialization
- Transport and communication
- Settlement
NB: Nyika means wilderness or open grassland
A CROSS- SECTION OF THE EAST AFRICAN RIFT VALLEY PLATEAU.
Ref: Fountain SST book 6.page 8 fig, 5.
COASTAL PLAINS OF E.AFRICA
- This refers to the narrow strip or edge of land which boarders the Indian Ocean.
- It widens to the north of Mombasa and south of Dar-es-salam and is about 64km wide and 18m above the sea level.
- It separates the Indian Ocean from the Eastern plateau
- It also contains the island of Pemba, Zanzibar and Mafia.
FEATURES FOUND ON THE COASTAL PLAINS
- Rivers
- Coral reefs
- Coastal harbours.
- Beaches
- Sea ports
- Oil refinaries
A Coral reef is limestone rock formedfrom skeleton of dead tiny marine animals called polyps.
- Provides limestone used for making cement
- Serve as a coastal harbour
- Its used for Tourism
Dangers of coral reefs
- Can hinder transport on water
ACTIVITIES DONE IN COASTAL PLAINS.
- Trade
- Mining
- Oil refining
- Tourism
- Transport and communication.
- Fishing
- Lumbering
- Farming
QUESTIONS.
1. Identify four major reliefs regions of E.Arica.
2. Give any two economic values of coral reefs to E.A.
3. State any two economic values of the coastal plains to the people of E.A.
4. Mention two tourist attractions found at the coast of E. Africa.
5. How are coral reefs a hindrance to water transport?
6. Why is Mombasa hotter than Mbale?
LAKES OF EAST AFRICA.
A lake is a depression or ahallow on the earth’s surface filled with (by) water.
EXAMPLES OF LAKES.
- L.Victoria
- L.Tanganyika.
- L.Kyoga.
- L.Magadi
- L.Wamala
- L.Nabugabo
- L.Turkana
TYPES OF LAKES IN E.A.
1. Depression (basin) lakes/down warped lakes; these can also be called down warping lakes.They were formed by the process of down warping.eg.
- L.Victoria
- L.Kyoga
- L.Kwania
- L.Amboseli in Kenya.
CHARACTERISTICS OF BASIN/DEPRESSION LAKES.
- They have fresh waters because they have outlets.
- They are wide.
- They are Shallow.
- They have swampy surroundings.
- They have irregular shape
2. RIFT VALLEYLAKES/FAULTY LAKES
- They are found on the rift valley floor.
- They were formed by the process of poultry.
Examples.
- L.Tanganyika
- L.Turkana
- L.Albert
- L.Edward.
CHARACTERISTICS OF RIFT VALLEY LAKES
- They are deep.
- They are long and narrow.
- They have salty water because they don’t have outlets.
Some rift valley lakes have fresh waters b’se they have outlets eg.L.Naivasha, L.Tanganyika, L. Albert, and .L.Malawi.
TYPES OF LAKES
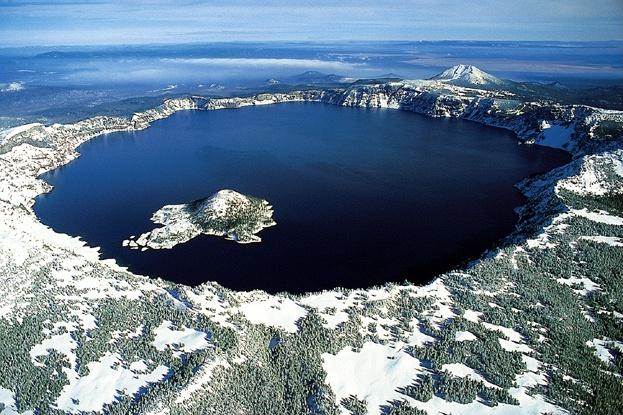
CRATER LAKES.
These are lakes formed by volcanicity.They are commonly found on top of dormant or deadvolcanoes.
Examples of crater lakes;
- L.Ngorongoro.
- L.Katwe
- Mt.Muhavura Crater Lake.
- Mt .Elgon crater lake
Some times crater lakes can be reffered to as calderas when secondary eruption takes place and they become wide.
DIAGRAM SHOWING A CRATER LAKE.

LAVA DAMMED LAKES.
These are lakes formed when lava blocks water from the main stream which makes water to be collected in one area/place.
Examples of lava Dammed lakes.
- L.Bunyonyi-deepest in Uganda.
- L.Bulela
- L.Mutanda.
MAN MADE LAKE;
These are lakes formed by acivities of man eg.Dam construction, brick making,digging, ponds etc.
Examples
- Kabaka’s lake.
- Kajjansi lake
- Namungongo Lake.
OX-BOW LAKES.
These are lakes formed by rivers meander and deposition.
Oxbow lakes can be seen along river Semliki and river Rwizi
VALUES OF LAKES TO MAN.
- They help in formation of rain.
- They attract tourists
- Some are used for mining of minerals.
- They are used for transport.
- They provide water for domestic and industrial use.
- Promote trade between territories.
- They are fishing grounds
- Lake shores are sources of sand
MAP SHOWING LAKES IN EAST AFRICA
QUESTION.
1. Why do many tourists prefer visiting lakes of E.Africa?
